外泌体分离提取鉴定最原始最权威的文献
Thery, C., et al. (2006). "Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids." Curr Protoc Cell Biol Chapter 3: Unit 3 22.
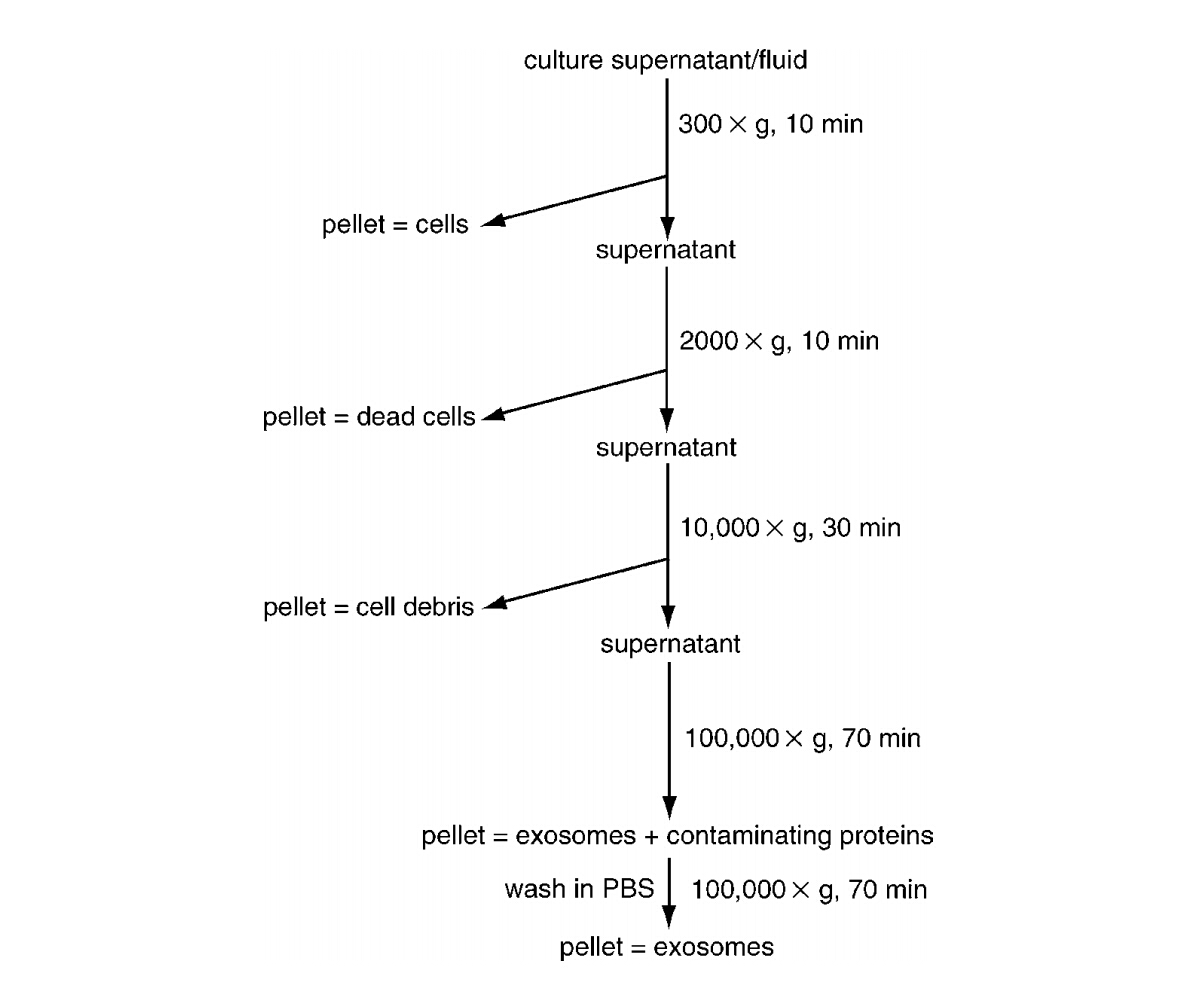
Exosomes are small membrane vesicles found in cell culture supernatants and in different biological fluids. Exosomes form in a particular population of endosomes, called multivesicular bodies (MVBs), by inward budding into the lumen of the compartment. Upon fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane, these internal vesicles are secreted. Exosomes possess a defined set of membrane and cytosolic proteins. The physiological function of exosomes is still a matter of debate, but increasing results in various experimental systems suggest their involvement in multiple biological processes. Because both cell-culture supernatants and biological fluids contain different types of lipid membranes, it is critical to perform high-quality exosome purification. This unit describes different approaches for exosome purification from various sources, and discusses methods to evaluate the purity and homogeneity of the purified exosome preparations.
外泌体分离提取流程图
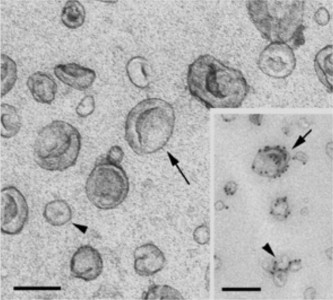
透射电镜显示的典型外泌体的形态结构
文献下载:
需要APPENDIX 2A和 SUPPLIERS APPENDIX的话,请下载2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology的全文:
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part01
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part02
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part03
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part04
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part05
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part06
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part07
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part08
2006-Current Protocols in Cell Biology.part09
外泌体资讯网 外泌体分离提取鉴定最原始最权威的文献