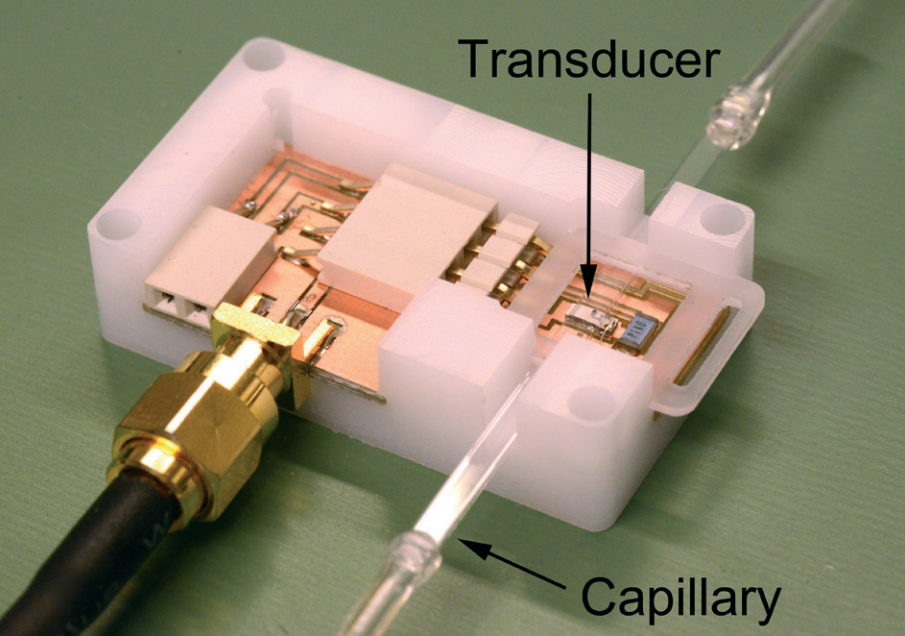
如何同小体积的血浆中分离出细胞外囊泡呢?而且最好不直接接触到这些细胞外囊泡,来自瑞典隆德大学的研究人员开发了一种可以从小体积血浆中通过非接触声波捕获细胞外囊泡的方法。
微粒(Microparticles,MP)是由细胞受到激活、压力或凋亡等反应时释放的大小为100-1000 nm的细胞外囊泡。研究发现血小板来源的MP(Platelet-derived MP,PMP)可以反映心血管疾病的病理生理过程,并且在临床上具有潜在可作为生物标志物的应用价值,以及需要更好地理解这些囊泡的生物学特性。目前用于分离MP的方法主要是差速离心法,这需要相当大的样品体积,并影响MP的完整性和组成成分。来自瑞典隆德大学的研究人员开发了一种基于微尺度声波技术快速、非接触式富集MP的新方法。从血浆分离的PMP通过扫描电子显微镜和流式细胞仪进行检测。此外,该检测系统的效果与待检测血浆样品的浓度和流速有关。最后,该技术与标准超速离心相比,具有快速简便自动化、非接触、样品需求量少和回收率高等优点。使用来自健康对照和ST段抬高心肌梗死(STEMI)的患者样品采样的标准差速离心协议。
版权归外泌体之家所有,欢迎转载,但请注明出处和原文链接!
Evander, M., et al. (2015). "Non-contact acoustic capture of microparticles from small plasma volumes." Lab Chip 15(12): 2588-2596.
Microparticles (MP) are small (100-1000 nm) membrane vesicles shed by cells as a response to activation, stress or apoptosis. Platelet-derived MP (PMP) has been shown to reflect the pathophysiological processes of a range of cardiovascular diseases and there is a potential clinical value in using PMPs as biomarkers, as well as a need to better understand the biology of these vesicles. The current method for isolating MP depends on differential centrifugation steps, which require relatively large sample volumes and have been shown to compromise the integrity and composition of the MP population. We present a novel method for rapid, non-contact capture of PMP in minute sample volumes based on a microscale acoustic standing wave technology. Capture of PMPs from plasma is shown by scanning electron microscopy and flow cytometry. Furthermore, the system is characterized with regards to plasma sample concentration and flow rate. Finally, the technique is compared to a standard differential centrifugation protocol using samples from both healthy controls and ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patient samples. The acoustic system is shown to offer a quick and automated setup for extracting microparticles from small sample volumes with higher recovery than a standard differential centrifugation protocol.
外泌体资讯网 一种从小体积血浆中非接触声波捕获细胞外囊泡的方法