骨质疏松症是一种以骨量减少、微观结构破坏和脆性骨折为特征的疾病,在老年群体中的发病率尤其高。骨质疏松性骨折,尤其是髋部骨折和椎体压缩骨折,是其最常见、最具破坏性的并发症,给患者带来巨大的身心痛苦,严重降低生活质量。随之增长的残疾率和死亡率给各个家庭和整个社会造成了沉重的经济负担。
现有的骨质疏松症治疗各自存在某些局限性。因此,研究者对干细胞移植和外泌体治疗这类新兴疗法对骨质疏松症的作用展开研究。干细胞由于其具有快速增殖、低免疫原性及多向分化能力,已被广泛应用于生物医学领域。基于此,干细胞来源的外泌体由于表面缺乏主要组织相容性复合体蛋白表达,因此基本不会发生免疫排斥反应,存在巨大的临床转化潜力。
Stem Cell Therapy & Research(中科院二区,影响因子8.079)在近期发表了福建医科大学附属第二医院脊柱外科俞海明教授、神经代谢调控中心林树教授团队的题为“Osteoporosis treatment using stem cell-derived exosomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies”的系统综述和荟萃分析(2023 Apr 11;14(1):72),聚焦于干细胞来源外泌体治疗骨质疏松动物模型相关的基础研究,该文第一作者为硕士研究生何晓钰。
该文最终纳入了2019-2022年期间的11项研究,共计15个实验,总样本量为242只动物,其中121只接受外泌体治疗,其余接受安慰剂治疗。实验涉及多种骨质疏松模型,外泌体来源涵盖尿液干细胞、胚胎干细胞、人脐带间充质干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞。
表1. 纳入研究的基础信息
| Study | Year | Experimental subject | Model | Sex | Age | Weight |
| Chen 1 | 2019 | Mice | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | / | / |
| Chen 2 | 2019 | Mice | Senile osteoporosis model | Unspecified | / | / |
| Chen 3 | 2019 | Mice | Disuse osteoporosis model (TS-induced osteoporosis model) | Unspecified | / | / |
| Gong | 2020 | SAMP8 mice | Senescence-accelerated model | Male | 6 months old | / |
| Hu 1 | 2020 | C57BL/6 mice | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | 8 weeks old | / |
| Hu 2 | 2020 | C57BL/6 mice | Senile osteoporosis model | Male | 16 months old | / |
| Hu 3 | 2020 | C57BL/6 mice | Disuse osteoporosis model (TS-induced osteoporosis model) | Unspecified | 3 months old | / |
| Huang | 2021 | SD rats | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | 10 weeks old | 230–250 g |
| Li | 2021 | SD rats | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | 8 weeks old | 294±11 g |
| Lu | 2020 | C57BL/6J mice | / | Male | 3 months old | / |
| Qiu | 2021 | SD rats | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | 12 weeks old | 280–300 g |
| Wang | 2022 | C57BL/6 mice | OVX-induced osteoporosis model | Female | 12 weeks old | 28–30 g |
| Xiao | 2021 | C57BL/6J mice | Disuse osteoporosis model (HU-induced osteoporosis model) | Male | 6 months old | / |
| Zhang | 2021 | SD rats | Diabetic osteoporosis model (STZ-induced diabetes) | Unspecified | 8–10 weeks old | / |
| Zhang | 2022 | SD rats | Diabetic osteoporosis model (STZ-induced diabetes) | Male | 8 weeks old | / |
OVX: ovariectomy; TS: tail suspension; SAMP8: senescence-accelerated mouse prone eight; SD: Sprague Dawley; HU: hindlimb unloading; STZ: streptozotocin
表2. 纳入实验的特征
| Study | Year | Source of exosomes | Administration route | Treatment cycle | Frequency | Sample area |
| Chen 1 | 2019 | USC (human) | Intravenous injection | 2 months | Once a week | Femur |
| Chen 2 | 2019 | USC (human) | Intravenous injection | 3 months | Once a week | Femur |
| Chen 3 | 2019 | USC (human) | Intravenous injection | 3 weeks | Twice a week | Femur |
| Gong | 2020 | ESC (human) | Gavage | 6 months | Once every other day | Femur |
| Hu 1 | 2020 | UCMSC (human) | Intravenous injection | 2 months | Once a week | Femur |
| Hu 2 | 2020 | UCMSC (human) | Intravenous injection | 3 months | Once a week | Femur |
| Hu 3 | 2020 | UCMSC (human) | Intravenous injection | 21 days | Twice a week | Femur |
| Huang | 2021 | BMSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 8 weeks | Once a week | Femur |
| Li | 2021 | BMSC (human) | Intravenous injection | 28 days | Once a week | Tibia |
| Lu | 2020 | BMSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 2 months | Twice a week | Femur |
| Qiu | 2021 | BMSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 2 weeks | / | Femur |
| Wang | 2022 | BMSC (rat) | Periosteum injection | 1 week | Twice a week | Femur |
| Xiao | 2021 | BMSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 4 weeks | Twice a week | Femur |
| Zhang | 2021 | ADSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 42 days | Once every other day | / |
| Zhang | 2022 | ADSC (rat) | Intravenous injection | 12 weeks | Once every other day | Femur and tibia |
USC: urine-derived stem cell; ESC: embryonic stem cell; UCMSC: umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cell; BMSC: bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; ADSC: adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
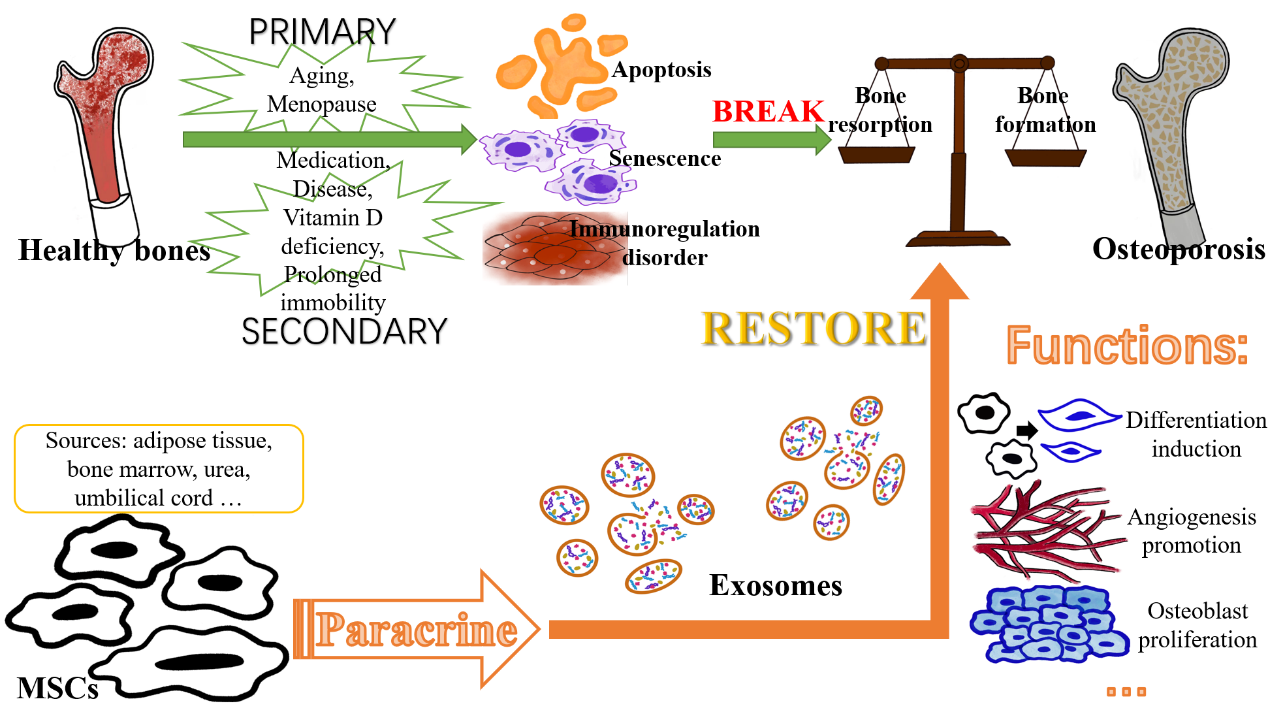
骨质疏松症的发病机制及外泌体的形成与释放机制示意图
干细胞来源的外泌体在具备抑制炎症、促进血管生成等干细胞功能的同时,不存在致癌、血栓形成等干细胞移植风险和伦理问题。此外,它具有更强大、广泛的生物功能,包括修复受损MSC和诱导成骨分化等,内含的核酸(miRNA、lncRNA和piRNA等)、蛋白质、脂质和其他活性物质通过细胞交流在骨修复中起到关键作用。干细胞来源的外泌体可促进细胞功能恢复,维持内部环境的稳态,通过不同的信号通路促进诱导分化、成骨细胞增殖、细胞凋亡抑制、血管生成和免疫调节,启动骨的修复和再生,从而改善骨量降低和骨质流失。
这篇荟萃分析选取6项骨相关指标(BMD, BV/TV, Tb. N, Tb. Th, Tb. Sp,和Ct. Th)评估其对骨质疏松动物模型的疗效,总体结果表明,干细胞来源的外泌体治疗可以改善骨质疏松症的骨修复和骨再生能力,对治疗动物模型中的骨质疏松症具有显著疗效。同时,对这类研究的局限性进行了探讨,希望对相关研究方案的完善有所帮助,并期望对这一疗法向临床转化起到一定的推动作用。
参考文献:
Osteoporosis treatment using stem cell-derived exosomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03317-4.
外泌体资讯网 Stem Cell Res Ther|福建医科大学附属二院俞海明/林树:干细胞来源外泌体治疗骨质疏松症的临床前研究进展与荟萃分析





